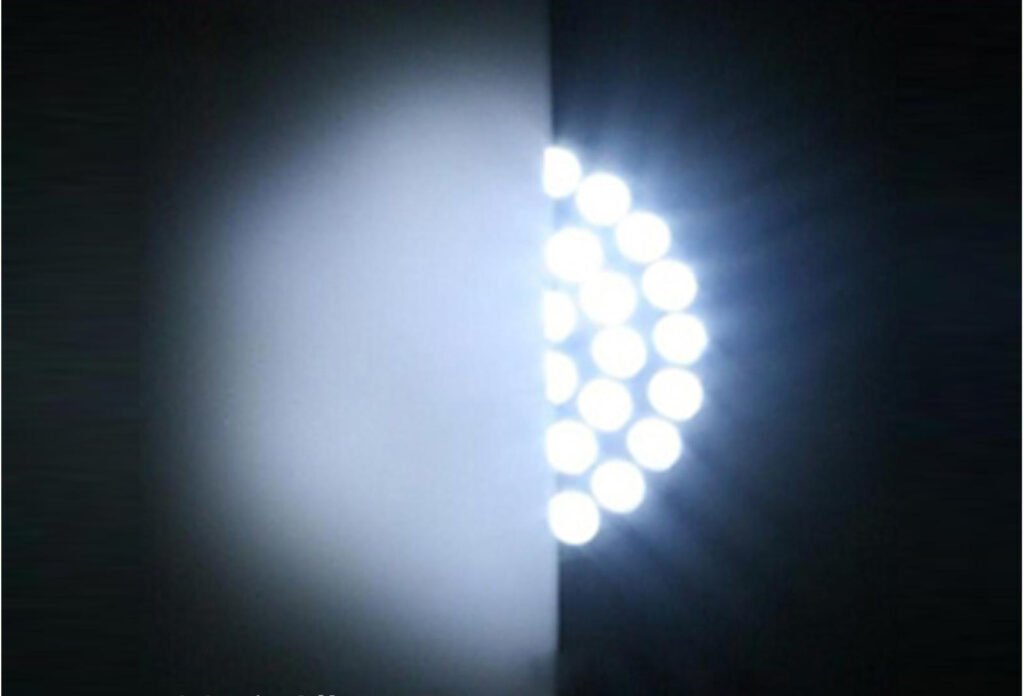
1. 빛 확산이란 무엇인가요?
광확산제는 빛을 산란시켜 눈부심을 줄이고 균일한 조명을 만들기 위해 기질(예: 플라스틱, 코팅)에 포함된 물질입니다. 일반적인 형태는 폴리머, 도자기, 광물 등의 입자 또는 첨가제로 구성됩니다.
2. 어떻게 작동하나요?
기본 소재와 굴절률이 다른 미세한 비트를 통해 빛을 산란시켜 광선이 구부러지고 퍼져 부드럽고 고른 조명을 만들어냅니다.
3. 일반적인 애플리케이션은 무엇인가요?
LED 조명, 스크린(LCD, OLED), 차량 조명, 광학 렌즈, 건물 코팅, 3D 프린팅에 활용되어 빛의 순환을 촉진합니다.
4. 어떤 유형이 제공되나요?
- 폴리머 기반 (예: PMMA, 실리콘).
- 무기물 (예: 실리카, 이산화티타늄).
- 하이브리드 여러 재료를 결합하여 효율성을 높입니다.
5. 최적의 광확산제를 선택하는 방법은 무엇인가요?
투명도, 기질 호환성, 복원력(열/자외선 저항), 적용 기술(코팅, 성형), 원하는 헤이즈/선명도를 위한 비트 치수를 고려하세요.
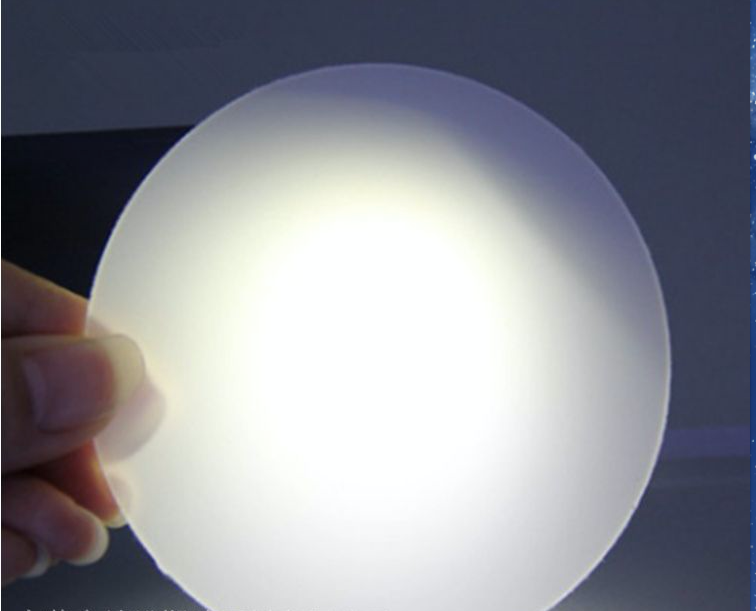

6. 안전한가요?
대부분은 안전하지만 보안은 다양합니다. MSDS를 검토하고 RoHS(전자제품) 또는 FDA(식품 접촉 제품)와 같은 법률을 준수하는지 확인하고 Reach 인증서를 확인하세요.
7. 환경에 미치는 영향?
일부는 VOC 또는 생분해되지 않는 성분을 함유하고 있습니다. 친환경 옵션(바이오 기반, 저-VOC)이 등장하고 있습니다. 폐기 지침을 따르세요.
8. 효과는 어떻게 측정하나요?
- 헤이즈 (%): ASTM D1003은 산란광을 측정합니다.
- 선명도: 균일성을 정량화합니다.
- 총 광 투과율: 확산과 밝기 손실 사이의 균형.
9. 빛 투과율이 감소하나요?
예, 하지만 고품질의 광확산제는 손실을 최소화합니다. 농도를 조정하면 확산과 밝기 사이의 균형을 최적화할 수 있습니다.
10. 시간이 지나면 성능이 저하되나요?
내구성은 소재에 따라 다릅니다. 자외선 차단제는 실외에서 사용합니다. 예상되는 조건(예: 열, 습도)에서 테스트합니다.
11. 신청 방법은?
- 성형 중 PC/PS/PMMA/PP와 같은 수지/플라스틱에 혼합하기
- 스프레이, 담그기 또는 브러싱을 통한 코팅.
- 3D 프린팅 필라멘트에 통합.
12. 호환성 문제가 있나요?
기질(플라스틱, 유리) 및 용매로 테스트합니다. 일부 약제는 구조적 무결성이나 접착력에 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다.
13. 어디서 구매하나요?
글로벌 유명 브랜드(Wacker, 다우, 시네스트),
완다 화학(중국 내 30년 전통의 광확산제 최대&선도 제조업체)
특수 광학 재료 공급업체. 산업용으로 사용할 수 있는 맞춤형 제형.
14. 비용 요인?
유형과 용량에 따라 다릅니다. 무기제(예: TiO₂)는 비용 효율적이며 고성능 폴리머는 더 비쌉니다. 대량 할인이 적용되는 경우가 많습니다.
15. 맞춤형 솔루션?
제조업체는 특정 투명도, 색상 또는 애플리케이션 요구 사항에 따라 맞춤형 입자 크기, 농도 또는 재료 혼합을 제공합니다.
16. 일반적인 문제?
- 고르지 않은 확산: 농도 또는 혼합을 조정합니다.
- 황변: 자외선 안정제를 사용합니다.
- 접착 문제: 표면 전처리(예: 플라즈마).
17. 새로운 트렌드?
- 정밀도를 위한 나노 입자.
- 바이오 기반/지속 가능한 에이전트.
- 스마트 확산(빛에 반응하는 소재).
18. 규정 준수?
애플리케이션에 따라 REACH(EU), RoHS(전자제품) 또는 UL(안전)과 같은 표준을 준수하는지 확인하세요.
19. 대안은?
디퓨저 필름, 에칭 유리 또는 미세 구조 표면. 에이전트는 통합과 비용 측면에서 유연성을 제공합니다.
20. 스토리지 권장 사항?
서늘하고 건조한 곳에 보관하세요. 습기를 피하세요(일부 약제는 뭉칠 수 있음). 유통기한은 일반적으로 1~2년이며 제조업체 지침을 확인하세요.
완다 화학 광확산제의 유통 기한: 2년
패키지를 개봉하지 않은 경우: 일부 고객 피드백에 따르면 3년 이내에도 계속 사용할 수 있습니다.
자세한 내용은 링크를 기록합니다: 광확산제

